CVE-2025-55182: React2Shell Detection and Fix Guide

UPDATE (Jan 1, 2026): RondoDox botnet now weaponizing React2Shell. Shadowserver reports 90,300 instances still vulnerable. Multiple nation-state actors actively exploiting. Patch immediately.
Wiz Research found vulnerable React versions in 39% of cloud environments they scanned. Half of exposed systems remain unpatched as of this week (Wiz). If you use Next.js App Router or React Server Components, you need to check your systems immediately. React2Shell has moved from proof-of-concept to multi-nation-state exploitation faster than almost any vulnerability in recent memory.
Update (December 17, 2025): This article has been updated with Microsoft threat intelligence on several hundred compromised machines, Iran-nexus threat actor attribution, Trend Micro's analysis of 145 in-the-wild PoCs, and a new React2Shell incident response section. CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell) is now confirmed as being used in ransomware campaigns.
Get threat intelligence like this delivered to your inbox. Subscribe to CyberDesserts for practical security insights, no fluff.
Quick Navigation
- What is React2Shell?
- Check If You Are Affected
- Detection and Scanning
- How to Fix It
- Incident Response
- WAF Mitigations
- Active Exploitation
- FAQs
What is React2Shell?
React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) is a critical unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in React Server Components. It carries a maximum CVSS score of 10.0 and allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable servers through a single malicious HTTP request. No authentication or user interaction is required.
The vulnerability affects the "Flight" protocol that React uses to communicate between client and server in React Server Components. Due to unsafe deserialization, attackers can craft payloads that bypass validation and execute code with the privileges of the server process.
React2Shell is being compared to Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228) due to its severity, ease of exploitation, and widespread impact across the software supply chain. Coalition Insurance notes that React and Next.js are downloaded a combined total of more than 72 million times weekly.
Having worked through Log4Shell in 2021, I see both similarities and differences here. The exploitation mechanics are simpler with React2Shell, requiring no chained lookups or environmental factors. But the attack surface is narrower since it only affects React 19 with Server Components, whereas Log4j was embedded everywhere from Minecraft servers to enterprise middleware. The real concern is the long tail. Organisations that patched Log4Shell in December 2021 were still finding vulnerable instances in obscure internal tools eighteen months later. Expect the same pattern here, particularly in containerised deployments where base images quietly inherit vulnerable dependencies.
React2Shell Timeline: Disclosure to Widespread Exploitation
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| Nov 29 | Lachlan Davidson discloses vulnerability to Meta |
| Dec 3 | Public disclosure; patches released by React and Vercel |
| Dec 4 | Working PoC published; China-nexus exploitation begins within hours (AWS) |
| Dec 5 | CISA adds to KEV catalog; Metasploit module released; Cloudflare WAF deployment causes global outage |
| Dec 5-8 | Surge in exploitation attempts (Trend Micro); Fastly reports 2,775% increase in attacks |
| Dec 7 | Burp Suite ActiveScan++ v2.0.8 released with React2Shell detection |
| Dec 8-10 | Unit 42 links exploitation to DPRK tooling; BPFDoor and Auto-color backdoors observed |
| Dec 12 | CISA remediation deadline passed; Google Cloud publishes SNOWLIGHT/COMPOOD threat intel; Iran-nexus actors observed; 50+ orgs confirmed breached |
| Dec 13 | CISA confirms React2Shell used in ransomware campaigns |
| Dec 15 | Microsoft confirms several hundred machines compromised; Defender for Cloud templates released |
Note: This vulnerability is also tracked as CVE-2025-66478 specifically for Next.js users. The NVD rejected this CVE as a duplicate of the main React CVE. The fix is identical.
Related RSC Vulnerabilities: Two additional flaws affecting React Server Components were disclosed alongside React2Shell. CVE-2025-55183 allows attackers to leak server function source code under specific conditions. CVE-2025-55184 enables denial-of-service through cyclical Promise references that trigger unbounded recursion. Cloudflare WAF rules cover all three CVEs. The primary concern remains CVE-2025-55182 due to its RCE capability.
The Flight Protocol Flaw
React Server Components use a protocol called "Flight" to pass data between browser and server. The React2Shell vulnerability is in how production servers deserialize incoming Flight requests. A malformed payload bypasses validation entirely, allowing attacker-controlled code to execute without authentication.
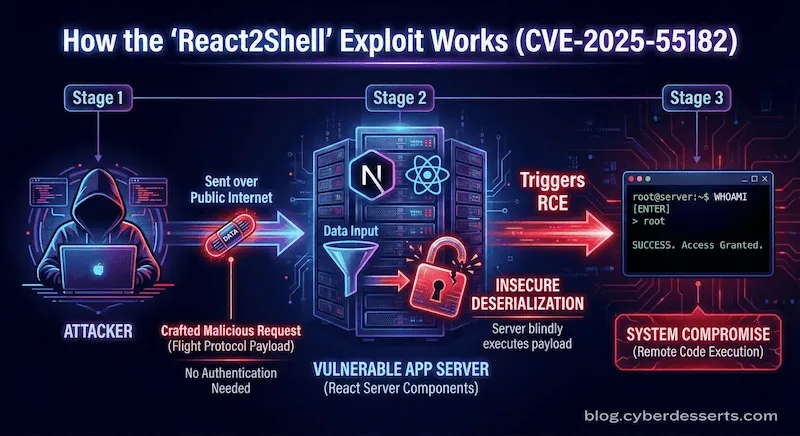
React2Shell attack flow: crafted payload → insecure deserialization → remote code execution
This is a runtime vulnerability. Your development environment and code repository are not at risk. Your live production servers accepting public traffic are. Standard deployments are vulnerable by default. A fresh Next.js app created with create-next-app can be exploited with no code changes by the developer (Wiz).
CVE-2025-55182 is a critical unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in React Server Components. It carries a maximum CVSS score of 10.0 and affects the "Flight" protocol used for server-side rendering. In testing, researchers achieved near 100% exploitation success rate (Wiz).
The Qualys research team describes the core issue: React's server runtime was never designed to handle untrusted input. Traditionally, client input is sanitized by APIs before server logic executes. React Server Components blurred that separation, allowing serialized data to travel directly between client and server without adequate validation.
Check If You Are Affected
Run this command in your project's root directory (where package.json lives):
npm list next react-server-dom-webpack react-server-dom-parcel react-server-dom-turbopack
This checks the dependency versions your project uses. If you have multiple applications, run this against each project. For containerized deployments, check your source project locally to identify the issue in your codebase.
Vulnerable React packages (versions 19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0):
- react-server-dom-webpack
- react-server-dom-parcel
- react-server-dom-turbopack
Vulnerable Next.js versions:
- Next.js 15.x prior to 15.0.5
- Next.js 16.x prior to 16.0.7
- Canary versions 14.3.0-canary.77 and later
Other affected frameworks that implement React Server Components include React Router, Waku, RedwoodSDK, Parcel RSC plugin, and Vite RSC plugin.
Next.js 13.x and 14.x stable releases using the Pages Router are generally not affected unless you manually implemented RSC features from unstable channels.
React2Shell Detection and Scanning
Security researchers have released scanner tools to help identify vulnerable applications at scale.
Assetnote Scanner: Tests for the vulnerability using safe-check mode that relies on side-channel indicators without executing code on your servers.
git clone https://github.com/assetnote/react2shell-scanner
cd react2shell-scanner
pip install requests tqdm
python scanner.py --safe-check -u https://your-app.com
The -u flag should point to your site that you are testing so as an example
python scanner.py --safe-check -u https://blog.cyberdesserts.com
The scanner looks for specific error responses that indicate a vulnerable Flight protocol implementation. By default it sends a crafted POST request that executes a deterministic math operation. Vulnerable hosts return the result in the X-Action-Redirect response header. The --safe-check flag uses an alternative detection method without executing code.
For CI/CD integration, community scanners now support GitHub Actions and SARIF output for automated security checks on pull requests. See the gensecaihq/react2shell-scanner repository for examples.
PoC Landscape Warning: Trend Micro has identified approximately 145 in-the-wild proof-of-concept exploits. However, most do not trigger the actual underlying React2Shell vulnerability. Some are AI-generated and non-functional.
"Before running ANY CVE-2025-55182 scanner, security teams are recommended to first verify against verified legitimate proof-of-concept exploits. Fake tools could be used to spread malware and cause a false sense of security." - Trend Micro Research
This is not theoretical. Trend Micro documented repositories that initially claimed to be functional exploits but were later updated to acknowledge their code was AI-generated and broken. Verify any scanner against known working PoCs before trusting the results.
Datadog IOCs: Detection rules for runtime environments are available at the Datadog indicators-of-compromise repository on GitHub.
Sysdig Falco Rules: The Sysdig Threat Research Team has developed Falco detection rules for React2Shell, available directly within Sysdig Secure.
Tenable Coverage: Tenable Cloud Security customers can scan for React2Shell across cloud workloads and Docker images. Tenable has published a detailed FAQ covering affected versions and detection guidance.
Scanning with Burp Suite
PortSwigger has updated Burp Suite with dedicated React2Shell detection capabilities. Penetration testers and security teams can now identify CVE-2025-55182 during routine application security assessments.
ActiveScan++ Extension (v2.0.8)
The ActiveScan++ BApp extension now includes specific checks for React2Shell. Install or update to version 2.0.8 via the BApp Store. The extension detects the Next-Action header anomalies and RSC error signatures associated with this vulnerability. No complex setup is required. Run a standard active scan and ActiveScan++ triggers its checks automatically (PortSwigger).
Dedicated Burp Extension
For more targeted scanning, a dedicated Next.js RSC RCE Scanner extension is available on GitHub. This extension implements the high-fidelity detection logic from SearchLight Cyber and checks for the specific RSC error signature (E{"digest") combined with a 500 status code to eliminate false positives.
To use the dedicated extension:
- Download the JAR from GitHub (tobiasGuta/Next.js-RSC-RCE-Scanner-Burp-Suite-Extension)
- Install via Extender > Extensions > Add
- Right-click any request and select Extensions > Next.js RSC RCE Scanner > Scan
- Check the Dashboard or Target tab for High Severity issues
PortSwigger notes that even if your application does not explicitly call server actions, it may still be vulnerable as long as it supports React Server Components.
Scanning with Metasploit
Rapid7 has released a Metasploit module for CVE-2025-55182 detection and exploitation. An unauthenticated check has been available to Exposure Command, InsightVM, and Nexpose customers since the December 4th content release.
For penetration testers using Metasploit Framework:
msfconsole
use auxiliary/scanner/http/react2shell_scanner
set RHOSTS target.com
run
Customers leveraging Rapid7's Intelligence Hub can track the latest developments including IOCs and Yara/Sigma rules. Rapid7 describes this as a "patch-now situation" given simultaneous exploitation from across the entire threat landscape.
How to Fix It
For React Server Components users, update to patched versions:
npm install [email protected]
# Or 19.1.2 or 19.2.1 depending on your version line
For Next.js 15 users:
npm install [email protected] react@latest react-dom@latest
For Next.js 16 users:
npm install [email protected] react@latest react-dom@latest
For Canary users, downgrade to stable v14 or upgrade to the latest fixed canary release.
Automated fix tool: Vercel has released an npm package to update affected Next.js apps. Run npx fix-react2shell-next or visit the GitHub page for the interactive tool.
Critical reminder: Patching requires rebuilding and redeploying your application. Simply updating package.json is not sufficient. You must rebuild and redeploy for the fix to take effect.
React2Shell Incident Response
If you believe your application may have been compromised, follow these incident response steps. This guidance is compiled from AWS, Microsoft, Vercel, and Wiz recommendations.
Prioritisation note: If you are managing multiple potentially affected systems, prioritise by exposure. Internet-facing applications with authentication backends or payment processing are highest risk. Internal tools on isolated networks can wait. Do not let the perfect be the enemy of the good here. Rotate your production database credentials and cloud API keys first, even before you have finished your full forensic investigation.
Immediate Actions
- Take the compromised server offline immediately. Do not attempt to fix it while running.
- Assume all secrets are compromised. Every secret in your .env file should be treated as exposed. Rotate immediately:
- Database passwords
- AWS Access Keys and GCP Service Account keys
- Payment API keys (Stripe, PayPal)
- JWT signing keys and NEXTAUTH_SECRET
- Any API tokens or credentials
- Do not attempt to clean malware manually. Attackers are skilled at hiding persistence mechanisms. Destroy the existing container, droplet, or EC2 instance entirely.
- Rebuild from source. Build a fresh instance from your patched source code. Do not restore from backups that may contain backdoors.
Forensic Investigation
Review logs for indicators of compromise:
- POST requests with
next-actionorrsc-action-idheaders - Unexpected process execution (whoami, id, cat /etc/passwd)
- File modifications in application directories
- Outbound connections to unknown IPs
- PowerShell arithmetic patterns like
powershell -c "40138*41979"(GreyNoise) - Access to cloud metadata endpoints (169.254.169.254)
Check for lateral movement:
- Did anyone download your database?
- Were new cloud instances spun up on your account?
- Are there new user accounts or modified authorized_keys files?
- Check for RMM tools like MeshAgent (Microsoft)
Reporting
- AWS customers: Open an AWS Support case for incident response assistance
- Wiz customers: Contact the Wiz Incident Response team
- Report to relevant authorities if personal data was exposed
Vercel advises: "If your application was online and unpatched as of December 4th, 2025 at 1:00 PM PST, we strongly encourage you to rotate any secrets it uses, starting with your most critical ones."
WAF and Runtime Mitigations
If you cannot patch immediately, major providers have deployed protections. WAF rules are a temporary measure. Patching remains the only safe fix.
| Provider | Protection Details | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudflare | Managed WAF rules automatically protect all customers proxying traffic. Note: Cloudflare's emergency deployment on Dec 5 caused a global outage affecting 28% of HTTP traffic. | None if WAF enabled |
| Vercel | WAF rules and runtime-level protections for all hosted projects. Some protections go beyond WAF rules. $25K-$50K bug bounty for protection bypasses. | None for hosted projects |
| Google Cloud | Cloud Armor WAF rules available for global and regional Application Load Balancers. GTIG published detailed threat intelligence on Dec 12. | Enable Cloud Armor rules |
| AWS | AWSManagedRulesKnownBadInputsRuleSet (v1.24+) includes CVE-2025-55182 rules. Sonaris active defense automatically blocks exploitation attempts. | Update to ruleset v1.24+ |
| Azure | Azure WAF custom rules available for Application Gateway and Application Gateway for Containers. Microsoft published rule guidance with ongoing updates. | Apply custom WAF rules |
| Fastly | Virtual Patch for NGWAF customers with automatic updates. Reported 2,775% increase in attacks within 24 hours of PoC. | Enable Virtual Patch |
| Akamai | Adaptive Security Engine Rapid Rules deployed for customers. | Enable ASE Rapid Rules |
Fastly verified that public PoCs grant attackers single-step ability to execute commands, exfiltrate data, and gain write access on vulnerable servers.
Active Exploitation: Nation-State and Cybercriminal Activity
React2Shell exploitation has expanded rapidly. Microsoft confirms several hundred machines compromised, with both Windows and Linux environments affected.
"We identified several hundred machines across a diverse set of organizations compromised using common tactics, techniques, and procedures observed with web application RCE." — Microsoft Security Blog, December 15, 2025
Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 has confirmed more than 50 organizations breached across the United States, Asia, South America, and the Middle East. Wiz Research has identified more than 15 distinct intrusion clusters (Microsoft, CyberScoop).
China-Nexus Activity
Amazon Web Services published detailed threat intelligence on React2Shell exploitation. Within hours of disclosure, AWS threat intelligence teams observed active exploitation attempts by multiple China state-nexus threat groups, including Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda (AWS Security Blog).
Unit 42 observed activity consistent with CL-STA-1015 (also known as UNC5174), a group suspected to be an initial access broker with ties to China's Ministry of State Security. This activity involved fileless execution of malicious shell scripts followed by the installation of SNOWLIGHT and VShell trojans (Unit 42).
Google Cloud Threat Intelligence (December 12)
Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) published detailed findings on widespread exploitation across multiple threat clusters. GTIG identified campaigns deploying MINOCAT tunneler, SNOWLIGHT downloader, HISONIC backdoor, and COMPOOD backdoor, as well as XMRIG cryptocurrency miners.
In separate incidents, suspected China-nexus threat actors UNC6586 and UNC6588 exploited the vulnerability to deploy SNOWLIGHT and COMPOOD backdoor payloads. GTIG also observed Iran-nexus actors exploiting CVE-2025-55182 (Google Cloud Blog).
North Korea-Linked Activity
Unit 42 uncovered activity that overlaps with previous attacks attributed to the North Korea threat group tracked as Contagious Interview, which has deployed EtherRAT tooling. Additional backdoors observed include BPFDoor (renamed KSwapDoor) and a new Auto-color variant (Unit 42).
Named Campaigns (Trend Micro)
Trend Micro identified distinct malware campaigns exploiting React2Shell:
- Emerald campaign: Deploys Cobalt Strike beacons generated with Cross C2
- Nuts campaign: Delivers Nezha, Fast Reverse Proxy (FRP), Sliver, and Secret-Hunter payloads
Both campaigns appear opportunistic rather than targeted, with high-volume scanning against cloud infrastructure including Vercel, AWS, and GCP (Trend Micro).
RondoDox Botnet (CloudSEK)
CloudSEK reported on January 1, 2026 that the RondoDox botnet has added React2Shell to its arsenal. The botnet campaign, active since early 2025, began exploiting CVE-2025-55182 in December to target IoT devices and web servers. Observed payloads include cryptocurrency miners, a botnet loader that terminates competing malware, and a Mirai variant. The loader continuously scans running processes and kills non-whitelisted executables every 45 seconds to prevent reinfection by rival actors.
Ransomware Connection
CISA's KEV catalog now lists CVE-2025-55182 as "Known to be used in ransomware campaigns." Rapid7 confirms their telemetry shows indicators linking vulnerability exploitation to tooling previously used by ransomware groups.
Behavioral Indicators for Detection
Defenders can use behavioral patterns observed in the wild by GreyNoise, Datadog, Microsoft, and Google:
- Unusual POST requests or traffic spikes to RSC/Server Function endpoints handling Flight payloads
- Unexpected errors related to deserialization or malformed RSC payloads in application logs
- Creation of unfamiliar temporary files near your application code following suspicious requests
- New outbound connections from app servers to untrusted IPs shortly after anomalous requests
- PowerShell execution patterns like
powershell -c "<digits>*<digits>"which indicate exploit validation (GreyNoise) - Reverse shells to Cobalt Strike servers (Microsoft)
- New malicious users or modified authorized_keys files (Microsoft)
- RMM tools such as MeshAgent used for persistence (Microsoft)
GreyNoise observed attackers using encoded PowerShell download-and-execute stagers with AMSI bypass techniques. If your detection platform supports it, aggregate detection on repeated PowerShell arithmetic patterns across a short window as a strong indicator of exploit validation.
C2 Infrastructure Indicators (Google Cloud):
- reactcdn.windowserrorapis[.]com (SNOWLIGHT C2)
- anywherehost[.]site
- interna1[.]site
Rapid7 customers can access Yara and Sigma rules for CVE-2025-55182 through the Intelligence Hub. Datadog Workload Protection customers can use custom rules to detect exploitation attempts in runtime. Microsoft Defender for Cloud customers can use security explorer templates to locate exposed containers and VMs.
Post-Exploitation Activity
Wiz Research, Unit 42, and Microsoft have published deep dives into post-exploitation behavior observed in compromised environments. Understanding these patterns helps security teams hunt for indicators of compromise beyond initial exploitation.
Credential Harvesting
Attackers establish shells to harvest credentials from environment variables, filesystems, and cloud instance metadata. Wiz identified actors attempting to extract AWS credentials and Base64 encode them for exfiltration. Look for unusual access to cloud metadata endpoints (169.254.169.254) from application containers.
Cryptomining Campaigns
Multiple cryptomining campaigns are leveraging React2Shell. Wiz observed attackers dropping UPX-packed XMRig variants with custom infrastructure that kills competing miners, attempts local privilege escalation, and masquerades as system processes like systemd-devd. Some campaigns pull stock XMRig from GitHub and run from writable locations like /tmp.
Backdoor Deployment
Post-exploitation payloads observed include:
- SNOWLIGHT/VShell: Multi-platform backdoor for remote access and lateral movement
- NoodleRAT (ANGRYREBEL): Cross-platform backdoor affecting Windows and Linux
- Cobalt Strike: Bash reverse shells connecting to Cobalt Strike servers; Cross C2 beacons
- BPFDoor (KSwapDoor): Linux backdoor
- Auto-color: Linux backdoor variant
- Mirai/Supershell/Rondo: Botnet loaders
- Sliver: Open-source C2 framework
- Secret-Hunter: Credential harvesting tool
- Nezha/FRP: Network tunneling tools
What is KSwapDoor?
KSwapDoor (previously tracked as BPFDoor) is a Linux backdoor observed in React2Shell post-exploitation activity. Unit 42 renamed it in their December 13 update after identifying distinct characteristics from the original BPFDoor malware.
KSwapDoor uses Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF) technology to monitor network traffic at the kernel level, allowing it to activate on specific "magic packets" without opening listening ports. This makes it particularly difficult to detect through traditional network scanning. The backdoor provides persistent remote access and has been associated with China-nexus threat actors exploiting CVE-2025-55182.
Defenders should look for:
- Unexpected BPF filters attached to network interfaces (
bpftool prog list) - Processes with deleted executables in /proc
- Unusual iptables rules that weren't administratively created
- Network connections that don't correspond to listening services
Persistence Mechanisms
Attackers are using nohup with disguised process names (e.g., /var/tmp/crond) as persistence mechanisms inside containers. Microsoft observed attackers adding new malicious users, deploying RMM tools like MeshAgent, modifying authorized_keys files, and enabling root login. Look for unexpected processes in /tmp or /var/tmp directories.
Summary
CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell) was added to CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog on December 5 with an accelerated remediation deadline of December 12 for federal agencies. That deadline has now passed. CISA has confirmed the vulnerability is being used in ransomware campaigns.
With React used by 82% of JavaScript developers according to the State of JavaScript 2024 survey, and Wiz finding vulnerable versions in 39% of cloud environments, this vulnerability has massive potential impact. The combination of unauthenticated access, near-perfect exploitation reliability, default-vulnerable configurations, and confirmed nation-state and ransomware activity makes immediate patching essential.
Shadowserver initially detected 77,664 vulnerable IP addresses on December 5, dropping to 28,964 by December 7. However, as of December 31, approximately 90,300 instances remain vulnerable worldwide, with 68,400 in the United States alone (Shadowserver Foundation). Microsoft confirms several hundred machines have already been compromised across Windows and Linux environments.
Looking ahead: The initial wave of opportunistic exploitation will subside as public-facing applications get patched. But React2Shell will have a long tail. Expect to see this CVE appearing in penetration test findings and breach reports throughout 2026, particularly in organisations with complex containerised deployments, legacy internal tools, and shadow IT. The vulnerability will also likely become a standard check in ransomware affiliate playbooks given its reliability and the value of the targets it exposes.
This is another reminder that supply chain and dependency security requires constant attention. For more on managing npm vulnerabilities effectively, see my npm Vulnerability Scanner guide and why continuous threat exposure is important.
Check your dependencies today and patch immediately.
This article gets updated as the threat landscape evolves. Subscribers receive notifications when major changes happen, plus weekly practical security content. No sales pitches, no fluff.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is React2Shell?
React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) is a critical unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in React Server Components. It allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable servers through a single HTTP request, with no authentication required. It carries a maximum CVSS score of 10.0.
What is KSwapDoor and how is it related to React2Shell?
KSwapDoor (formerly tracked as BPFDoor) is a Linux backdoor that Unit 42 observed being deployed after successful React2Shell exploitation. It uses Berkeley Packet Filter technology to hide at the kernel level, activating only on specific "magic packets" without opening visible listening ports. KSwapDoor has been associated with China-nexus threat actors targeting CVE-2025-55182 victims.
Is Next.js 14 safe from CVE-2025-55182?
Generally, yes. Next.js 14 (Stable/Pages Router) is safe. You are only at risk if you manually enabled the experimental React Server Components (RSC) features.
Does Cloudflare protect against React2Shell?
Yes, Cloudflare WAF has deployed automatic rules to block the malicious "Flight" protocol payloads for all proxied React applications. Note that Cloudflare's emergency deployment on December 5 initially caused a global outage affecting 28% of HTTP traffic, highlighting the complexity of protecting against this vulnerability.
Is this vulnerability exploitable without authentication?
Yes. An unauthenticated attacker can execute code on your server (RCE) by sending a crafted HTTP request. No user interaction or authentication is required.
Can I detect React2Shell with Burp Suite?
Yes. Update ActiveScan++ to v2.0.8 via the BApp Store or install the dedicated Next.js RSC RCE Scanner extension from GitHub for targeted scanning.
What is the CISA deadline for patching?
CISA initially set a December 26 deadline, then shortened it to December 12, 2025. That deadline has now passed. Federal agencies should have already remediated. All organizations should treat this as an emergency patch.
Is React2Shell being used in ransomware attacks?
Yes. CISA's KEV catalog now lists CVE-2025-55182 as "Known to be used in ransomware campaigns." Rapid7 confirms their telemetry shows indicators linking exploitation to tooling previously used by ransomware groups.
What should I do if my server was compromised?
Take the server offline immediately, assume all secrets are compromised and rotate them, destroy the instance rather than trying to clean it, and rebuild from patched source code. See the React2Shell Incident Response section above for detailed guidance.
What cloud providers have published threat intelligence?
AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft, and multiple security vendors have published detailed threat intelligence. Microsoft confirmed several hundred machines compromised as of December 15.
Last updated: 1st January, 2026
References and Sources
- React Team. (2025). "Critical Security Vulnerability in React Server Components." Official disclosure and patched versions.
- CISA. (2025). "Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog." CVE-2025-55182 added December 5. Deadline shortened to December 12. Confirmed use in ransomware campaigns.
- Microsoft Security Blog. (2025). "Defending against the CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell) vulnerability in React Server Components." December 15. Several hundred machines compromised, Windows and Linux affected, Defender for Cloud templates.
- Palo Alto Networks Unit 42. (2025). "Exploitation of Critical Vulnerability in React Server Components." Updated December 12-13 with 50+ confirmed breaches, North Korea-linked tooling, and expanded malware families.
- Google Threat Intelligence Group. (2025). "Multiple Threat Actors Exploit React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182)." December 12. SNOWLIGHT, COMPOOD, MINOCAT deployment; Iran-nexus actors observed.
- Trend Micro. (2025). "CVE-2025-55182: React2Shell Analysis, Proof-of-Concept Chaos, and In-the-Wild Exploitation." ~145 PoCs identified, emerald and nuts campaigns, surge Dec 5-8.
- AWS Security Blog. (2025). "China-nexus cyber threat groups rapidly exploit React2Shell vulnerability." Updated December 12. Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda attribution.
- Wiz Research. (2025). "React2Shell Deep Dive: CVE-2025-55182 Exploit Mechanics." 15+ intrusion clusters identified, 50% of exposed systems remain unpatched.
- Vercel. (2025). "Resources for protecting against React2Shell." Incident response guidance, secret rotation recommendations.
- CyberScoop. (2025). "Attacks pinned to critical React2Shell defect surge, surpass 50 confirmed victims." December 12.
- Qualys. (2025). "React2Shell: Decoding CVE-2025-55182 – The Silent Threat in React Server Components." December 10.
- Fastly. (2025). "React2Shell RCE Protection." 2,775% increase in attack attempts within 24 hours of PoC release.
- GreyNoise. (2025). "CVE-2025-55182 Opportunistic Exploitation In The Wild." 362 unique IPs observed, scanning patterns and behavioral indicators.
- Sysdig. (2025). "Detecting React2Shell." Falco detection rules.
- Datadog Security Labs. (2025). "CVE-2025-55182 React2Shell." IOCs and detection guidance.
- PortSwigger. (2025). "How to detect React2Shell with Burp Suite." ActiveScan++ v2.0.8 detection capabilities.
- Rapid7. (2025). "React2Shell Critical Unauthenticated RCE." Metasploit module, honeypot observations, ransomware tooling indicators.
- Cloudflare. (2025). "React2Shell and related RSC vulnerabilities threat brief: early exploitation activity and threat actor techniques." December 11. 582M WAF rule hits, scanner User-Agent patterns, Asian-nexus threat actor TTPs.
- CloudSEK. (2026). "RondoDox Botnet Weaponizes React2Shell." January 1. Nine-month campaign adds CVE-2025-55182 to target IoT devices and web servers.





Member discussion